Crafting a clear and comprehensive Software Business Requirements Document (BRD) is crucial for the success of any software development project. A well-defined BRD acts as the single source of truth, ensuring that all stakeholders are aligned on the goals, scope, and functionality of the software. Without a solid BRD, projects can quickly derail due to misunderstandings, scope creep, and ultimately, unmet business needs. To help streamline the process, utilizing a BRD template can save time, improve consistency, and ensure that all critical aspects are covered. This post provides a detailed overview of a Software BRD template, outlining the key sections and elements to include to create a robust and effective document.
Software Business Requirements Document Template
-
1. Introduction
- 1.1. Purpose: Clearly state the purpose of the document, outlining the scope of the software project and the intended audience for the BRD. This section should answer the question: “Why are we creating this document?”.
- 1.2. Scope: Define the boundaries of the project. What is included in the project and, equally important, what is *not* included? Explicitly stating what is out of scope can prevent misunderstandings later on.
- 1.3. Background: Provide context for the project. Explain the business problem or opportunity that the software aims to address. Include relevant information about the existing systems, processes, and market landscape.
- 1.4. Target Audience: Identify who will be using this document. This includes developers, testers, project managers, business analysts, and stakeholders. Knowing the audience helps tailor the language and level of detail appropriately.
- 1.5. Definitions and Acronyms: Define any technical terms, acronyms, or jargon that may be unfamiliar to the target audience. This ensures clarity and avoids ambiguity.
-
2. Business Goals and Objectives
- 2.1. Business Goals: Define the high-level strategic goals that the software is intended to achieve. These should be measurable and aligned with the overall business strategy. For example, “Increase customer satisfaction by 15% in the next quarter.”
- 2.2. Business Objectives: Specify the specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives that will contribute to achieving the business goals. These are the concrete steps that will be taken. For example, “Reduce customer service response time by 20%.”
- 2.3. Success Metrics: Identify the key performance indicators (KPIs) that will be used to measure the success of the project. These metrics should be directly linked to the business goals and objectives.
-
3. Stakeholder Analysis
- 3.1. Stakeholder Identification: List all the stakeholders who have an interest in the project. This includes internal stakeholders (e.g., management, employees) and external stakeholders (e.g., customers, partners).
- 3.2. Stakeholder Roles and Responsibilities: Define the role and responsibilities of each stakeholder in the project. Who is responsible for providing requirements? Who is responsible for approving the final product?
- 3.3. Stakeholder Needs and Expectations: Document the needs and expectations of each stakeholder group. This will help ensure that the software meets the needs of all users.
-
4. Functional Requirements
- 4.1. Feature List: Provide a comprehensive list of all the features that the software must include. Each feature should be described briefly and concisely.
- 4.2. Detailed Feature Descriptions: For each feature, provide a detailed description of its functionality. This should include:
- Input: What data does the feature require as input?
- Process: What processing steps are involved?
- Output: What is the output of the feature?
- User Interface (UI) Requirements: How will the feature be accessed and used through the UI? Mockups or wireframes can be included here.
- Error Handling: How will the software handle errors or unexpected input?
- 4.3. Use Cases: Describe how users will interact with the software to accomplish specific tasks. Use cases should be written from the user’s perspective and should include the steps involved, preconditions, and postconditions.
-
5. Non-Functional Requirements
- 5.1. Performance Requirements: Specify the performance requirements of the software, such as response time, throughput, and scalability. For example, “The system should be able to handle 1000 concurrent users.”
- 5.2. Security Requirements: Define the security requirements of the software, such as authentication, authorization, and data encryption.
- 5.3. Usability Requirements: Describe the usability requirements of the software, such as ease of use, learnability, and accessibility.
- 5.4. Reliability Requirements: Specify the reliability requirements of the software, such as uptime, availability, and fault tolerance.
- 5.5. Maintainability Requirements: Define the maintainability requirements of the software, such as code quality, documentation, and testability.
- 5.6. Portability Requirements: Specify the portability requirements of the software, such as platform compatibility and browser support.
-
6. Assumptions and Constraints
- 6.1. Assumptions: List any assumptions that are being made about the project, such as the availability of resources or the stability of the underlying infrastructure.
- 6.2. Constraints: Identify any constraints that may limit the scope or functionality of the project, such as budget limitations, time constraints, or regulatory requirements.
-
7. Open Issues and Risks
- 7.1. Open Issues: List any open issues that need to be resolved before the project can proceed.
- 7.2. Risks: Identify any potential risks that could impact the project, such as technical risks, market risks, or regulatory risks. For each risk, include a description of the risk, its potential impact, and mitigation strategies.
-
8. Appendix
- 8.1. Glossary: Include a glossary of terms used in the document.
- 8.2. References: List any references used in the document, such as external documents, websites, or standards.
- 8.3. Change Log: Track any changes made to the document, including the date, author, and description of the changes.
By following this template, you can create a comprehensive and well-organized Software Business Requirements Document that will help ensure the success of your software development project. Remember to tailor the template to your specific project needs and to involve all stakeholders in the process. Regularly reviewing and updating the BRD throughout the project lifecycle is crucial to maintaining its accuracy and relevance.
If you are searching about Technical Documentation In Software Development | Altexsoft With you’ve visit to the right place. We have 22 Images about Technical Documentation In Software Development | Altexsoft With like Software Business Requirements Document Template in Word, Google Docs, 40+ Simple Business Requirements Document Templates – Template Lab and also Download Free BRD Templates | Smartsheet. Here it is:
Technical Documentation In Software Development | Altexsoft With

www.pinterest.com
40+ Simple Business Requirements Document Templates ᐅ TemplateLab

templatelab.com
40+ Simple Business Requirements Document Templates ᐅ TemplateLab

templatelab.com
40+ Simple Business Requirements Document Templates – Template Lab

templatelab.com
Functional Requirements Template – Software Development Templates
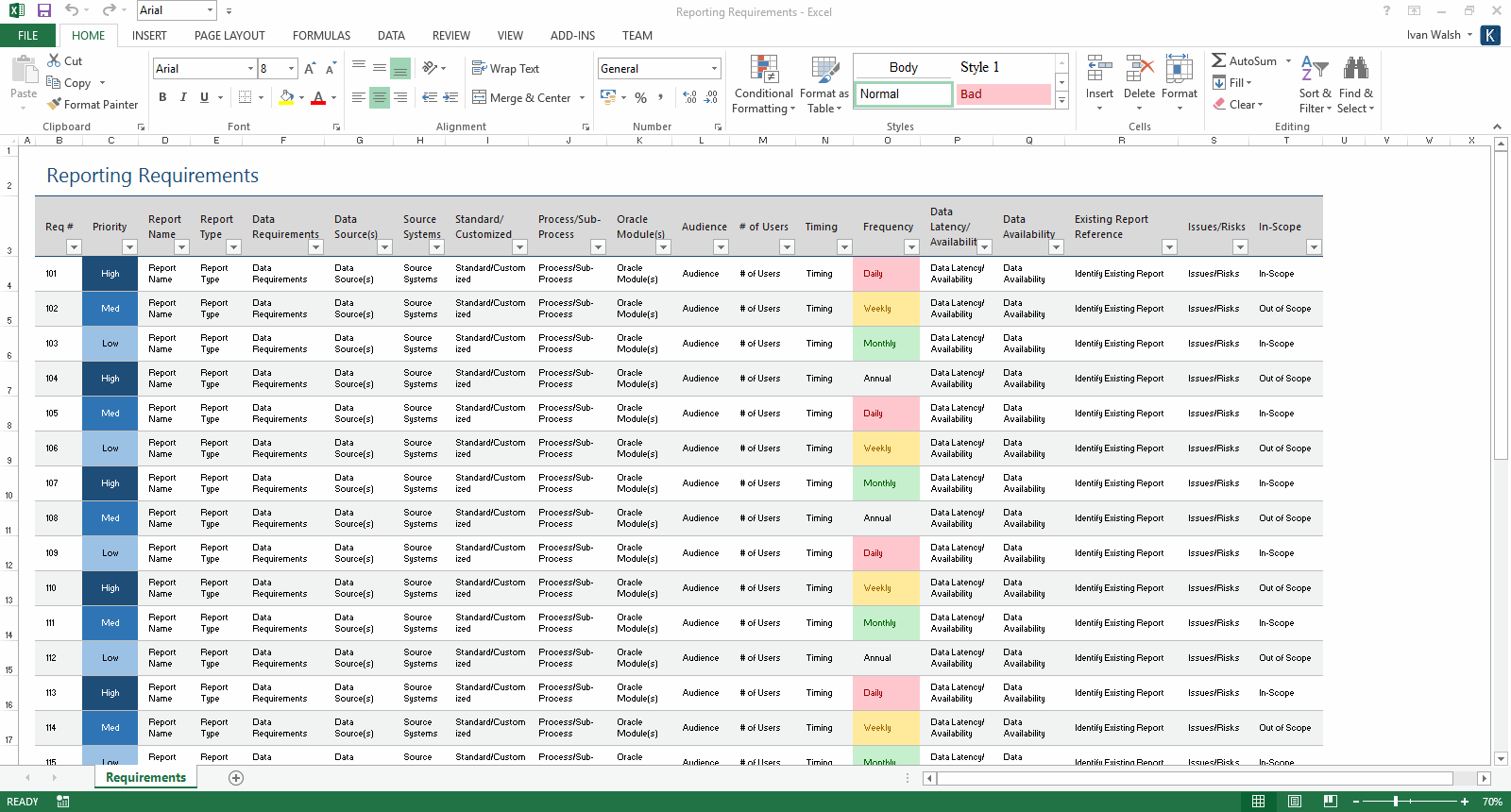
www.softwaredevelopmenttemplates.com
40+ Simple Business Requirements Document Templates – Template Lab
templatelab.com
Business Requirements Document (BRD) Template & Guide | EdrawMind

www.edrawmind.com
Functional Requirements Template – Software Development Templates

www.softwaredevelopmenttemplates.com
Business Requirement Specification Document Template – KAESG BLOG
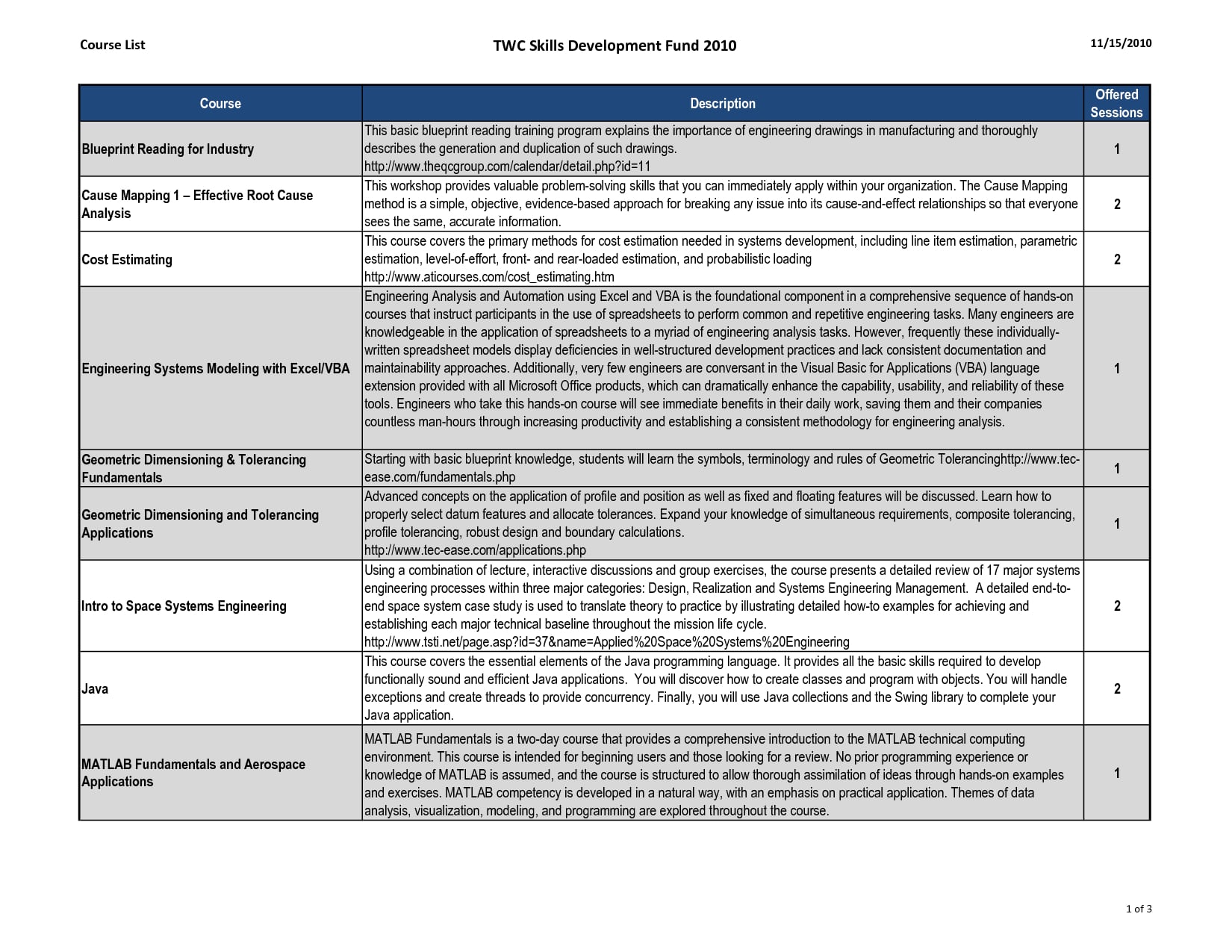
kaesg.com
Free Printable Business Requirements Document (BRD) Templates [PDF, Word]
![Free Printable Business Requirements Document (BRD) Templates [PDF, Word]](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/brd-business-requirement-document.jpg)
www.typecalendar.com
How To Write & Use A Business Requirements Document + Usable Outline

www.usemotion.com
40+ Simple Business Requirements Document Templates – Template Lab

templatelab.com
Sample Business Requirements Document Template In Word, Google Docs

www.template.net
Software Business Requirements Document Template In Word, Google Docs

www.template.net
Software Business Requirements Document Template In Word, Google Docs

www.template.net
Business Requirements Document Template: 7 Components [2022] • Asana
![Business Requirements Document Template: 7 Components [2022] • Asana](https://assets.asana.biz/m/22c11a35429c9c57/original/inline-business-strategy-business-requirements-document-template-1-2x.jpg)
asana.com
40+ Simple Business Requirements Document Templates – Template Lab

templatelab.com
40+ Simple Business Requirements Document Templates ᐅ TemplateLab
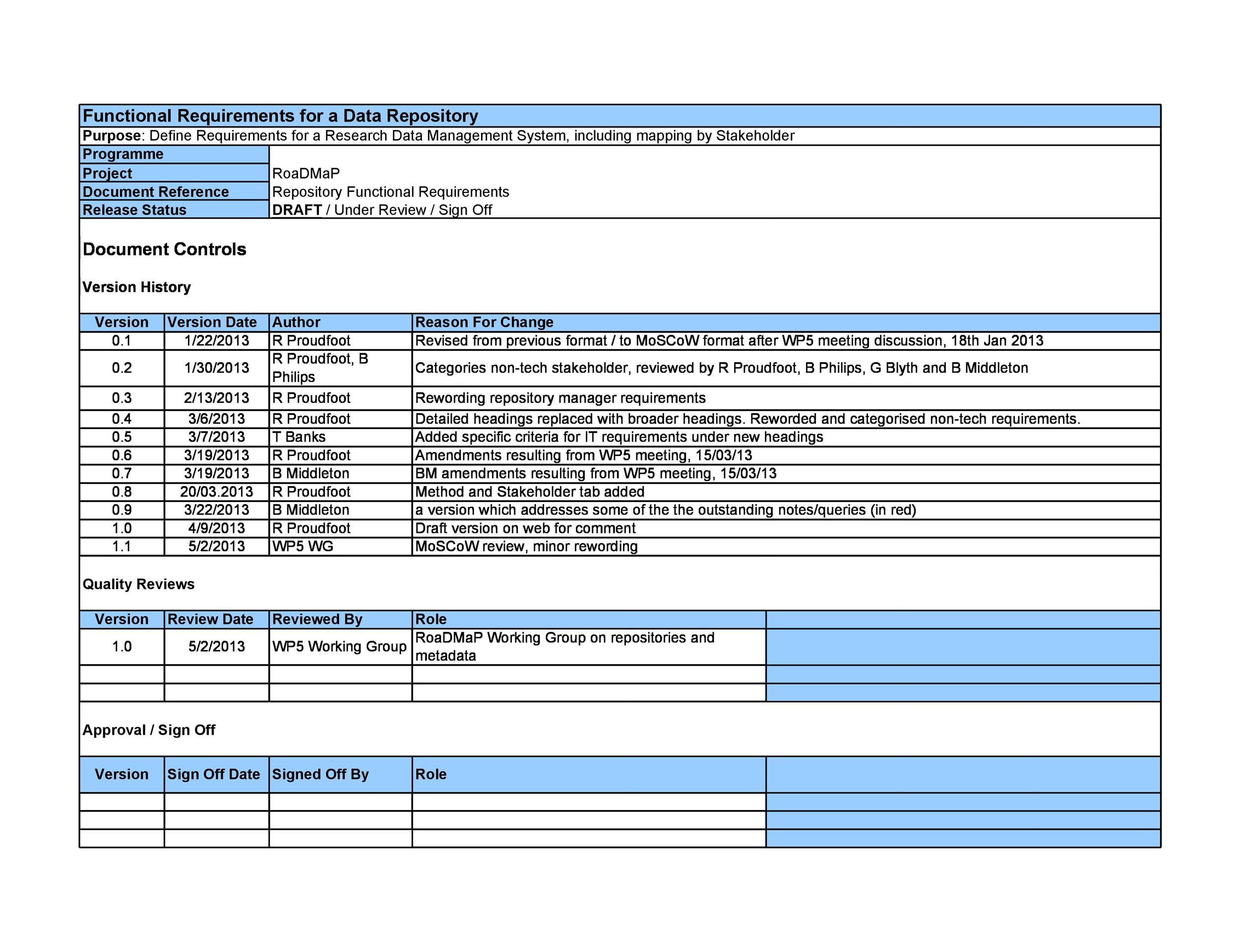
templatelab.com
Software Requirements Document: Definition, Steps And Template Included!

blog.bit.ai
Editable Business Requirements Document Templates In Word To Download

www.template.net
Download Free BRD Templates | Smartsheet
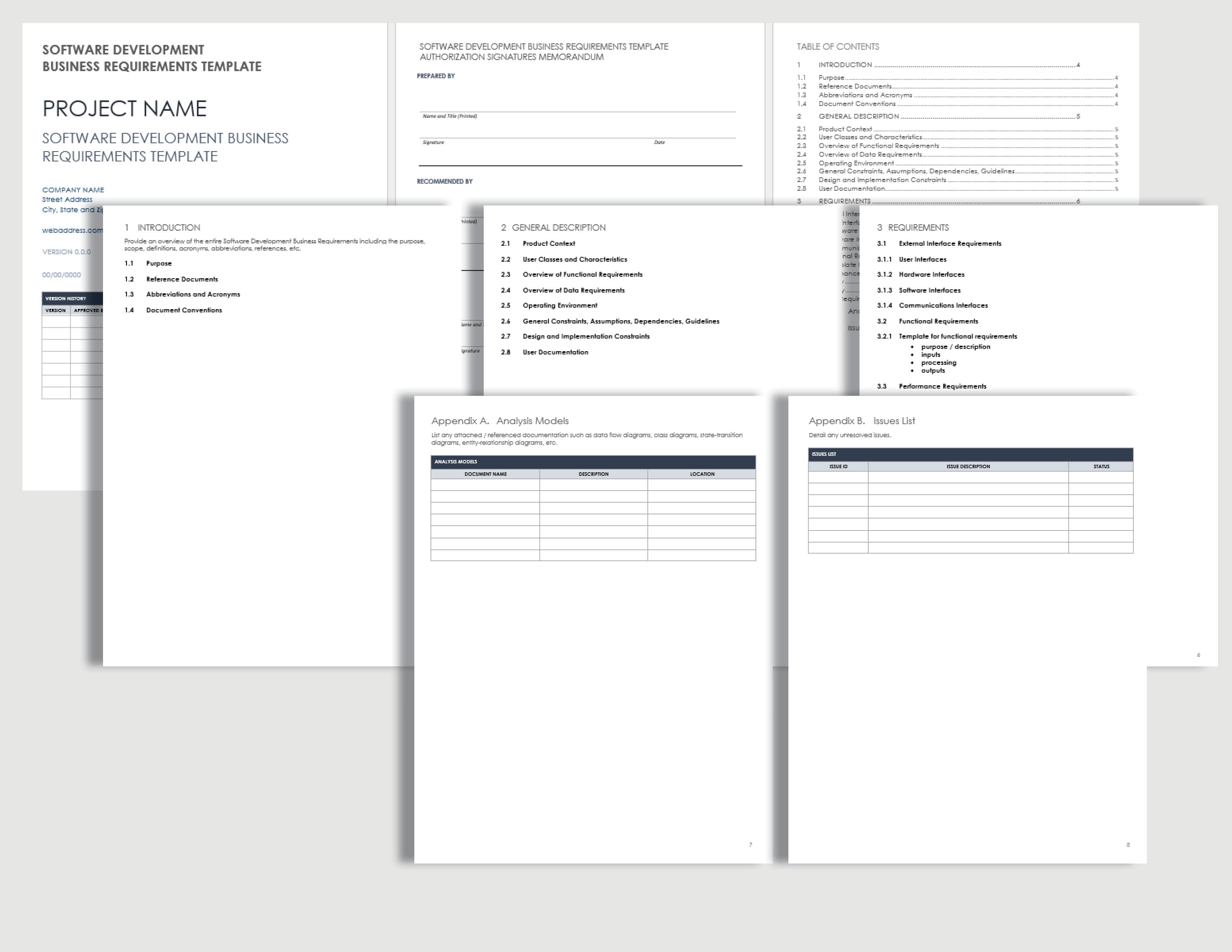
www.smartsheet.com
Download Free BRD Templates | Smartsheet
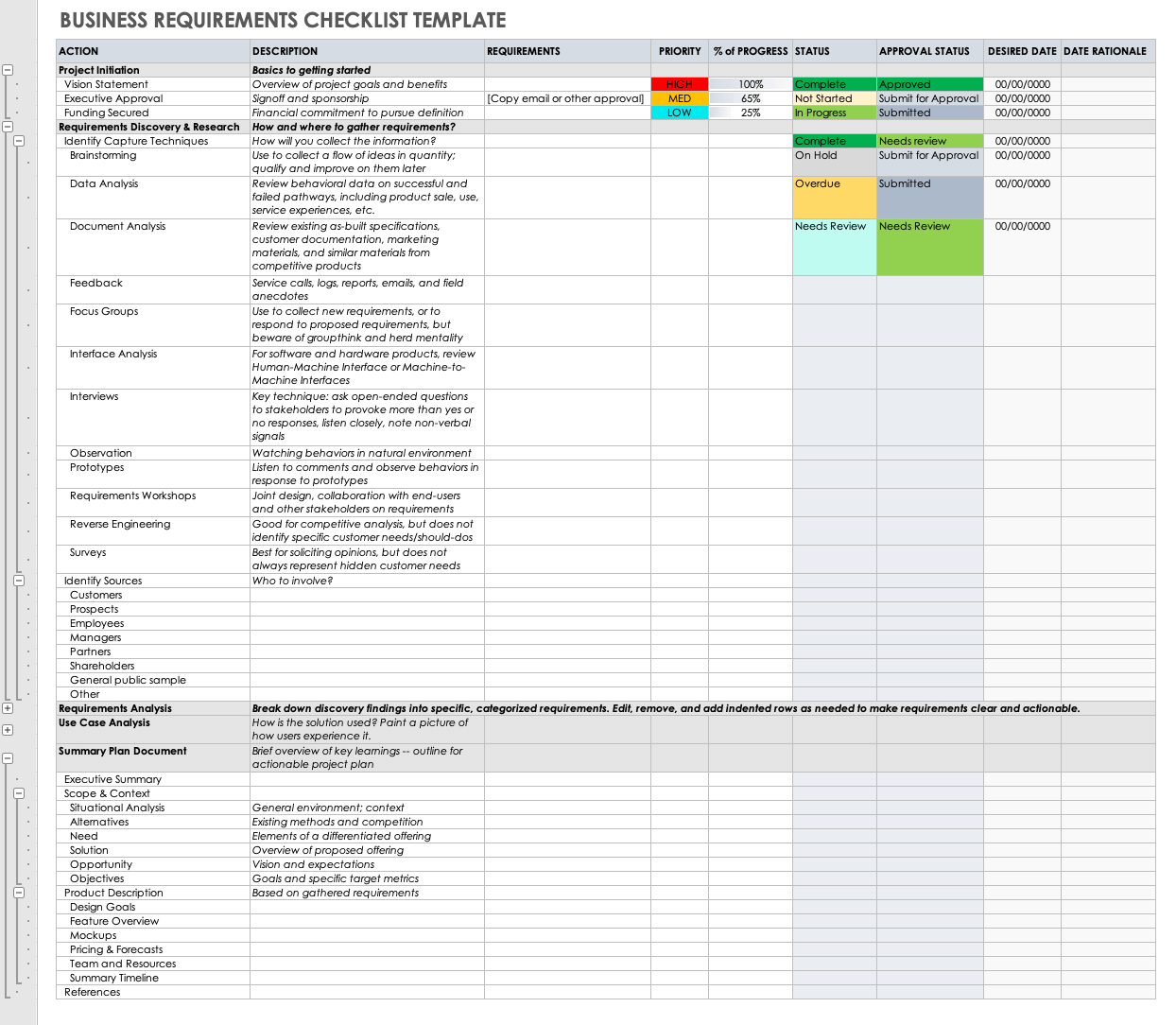
www.smartsheet.com
40+ simple business requirements document templates ᐅ templatelab. Functional requirements template – software development templates. business requirements document template: 7 components [2022] • asana